
This interesting feature of quantum chromodynamics prescribes that the effective interaction of the quarks should decrease in strength as the quarks interact in close proximity to each other, and this has been verified to be true in experiments. In a quark matter, the effective quark interaction is relatively weak, and perturbative treatment of the interaction is possible. The treatment of quark interaction turns out to be not as difficult as it is for neutrons.

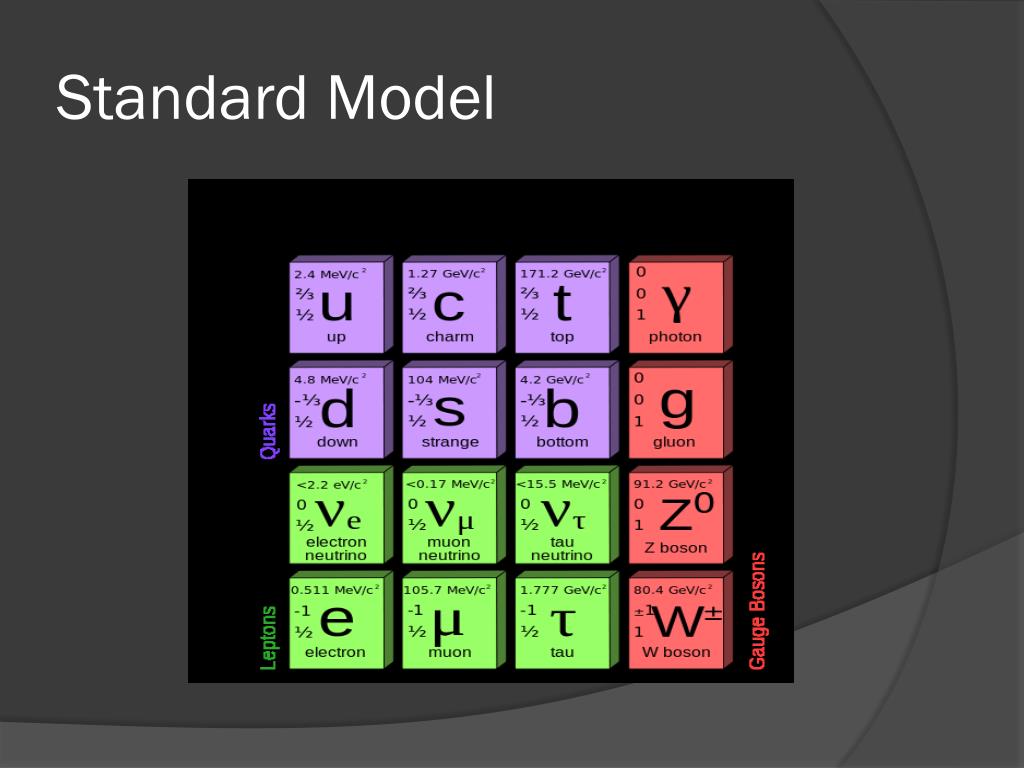
If quark interaction is neglected, the equation of state of quark matter may be deduced in the same manner as it is for a degenerate electron system. Inside a nucleon, their effective masses are estimated to be (expressed in mc 2) under 100 MeV for the u and d quarks, approximately 100–200 MeV for the s quark, and approximately 2000 MeV for the c quark. There are different species of quarks, and the known quarks are given the names of up quark (u), down quark (d), strange quark (s), and charm quark (c). Quarks are fermions and like electrons and neutrons obey Pauli's exclusion principle. When matter density reaches the point that the average separation of the nucleons is less than its confining radius, the individual identity of the nucleon is lost, and the matter system turns into a uniform system of quarks forming quark matter. The size of the nucleon is therefore determined by the confining radius of the quark interaction. In a quark model of the elementary particles, the nucleon is viewed as the bound state of three quarks, which interact via the exchange of gluons as determined by quantum chromodynamics. Y.C.Leung George, in Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (Third Edition), 2003 IV.G Quark Matter


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
